react系列-redux
基础
目的
状态管理器
JavaScript 需要管理的状态越来越多,越来越复杂;
这些状态包括服务器返回的数据、缓存数据、用户操作生产的数据等等,也包括一些 UI 的状态,比如某些元素是否被选中,是否显示加载动效,当前分页等;
当应用程序复杂时,state 在什么时候,因为什么原因而发生了变化,发生了怎样的变化,会变得非常难以控制和追踪。
定义
Redux 是 JavaScript 的状态容器,提供了可预测的状态管理。
跟框架无关,可以结合 vue 等其他框架使用。
核心理念
redux = reducer + flux
store
保存 state 数据
action
Redux 要求我们通过 action 来更新数据:
- 所有数据的变化,必须通过派发(dispatch)action 来更新;
- action 是一个普通的 JavaScript 对象,用来描述这次更新的 type 和 content;
reducer
reducer 将 state 和 action 联系起来
reducer 是一个纯函数
reducer 做的事情就是将传入的 state 和 action 结合起来生成一个新的 state
原则
单一数据源、单向数据流
store 是唯一的。
整个应用程序的state被存储再一颗 object tree 中,并且这个 object tree只存储在一个 store 中;
Redux 并没有强制让我们不能创建多个 Store,但是那样做不利于数据的维护;
单一的数据源可以让整个应用程序的 state 变得方便维护、追踪、修改;
State是只读的
唯一修改 State 的方法是触发 action,不要视图在其他地方通过任何的方式来修改 State;
这样可以保证所有的修改都被集中化处理,并且按照严格的顺序来执行,所以不需要担心 race condition(竞态)的问题。
只有 store 更改 state 数据内容,reducer 可以接受 state,但不能改变 state。
使用纯函数来执行修改
通过 reducer 将旧 state 和 actions 联系在一起,并且返回一个新的 state;
随着应用程序的复杂度增加,我们可以将 reducer 拆分成多个小的 reducers,分别操作不同 state tree的一部分;
所有的 reducer 都应该是纯函数,不能产生任何副作用。
redux 数据交互流程
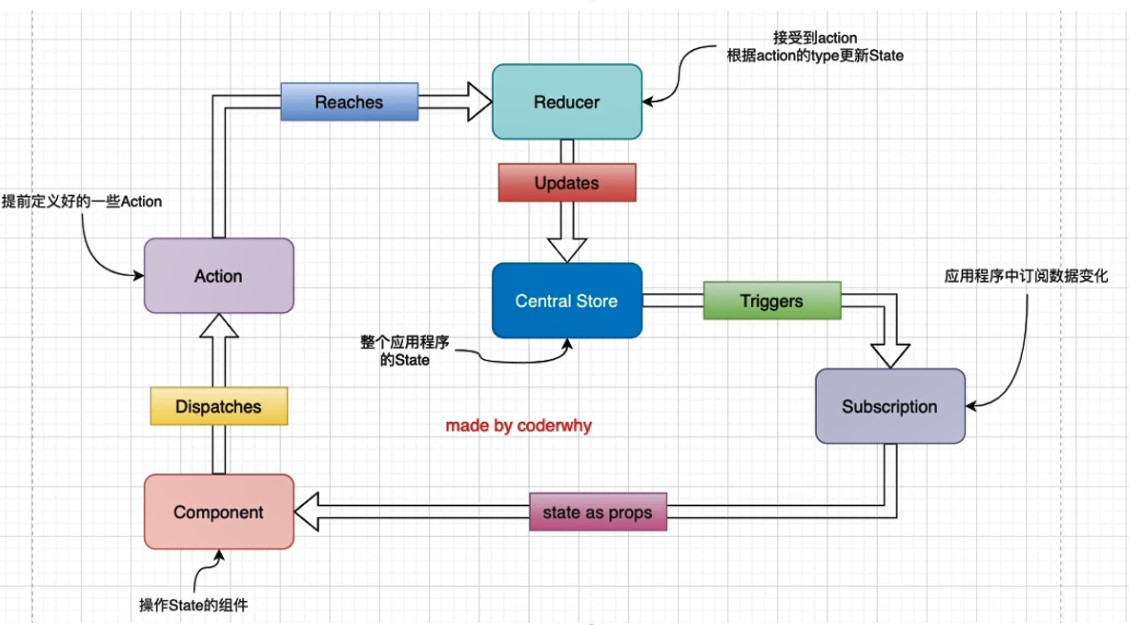
redux数据流动方向:单向数据流

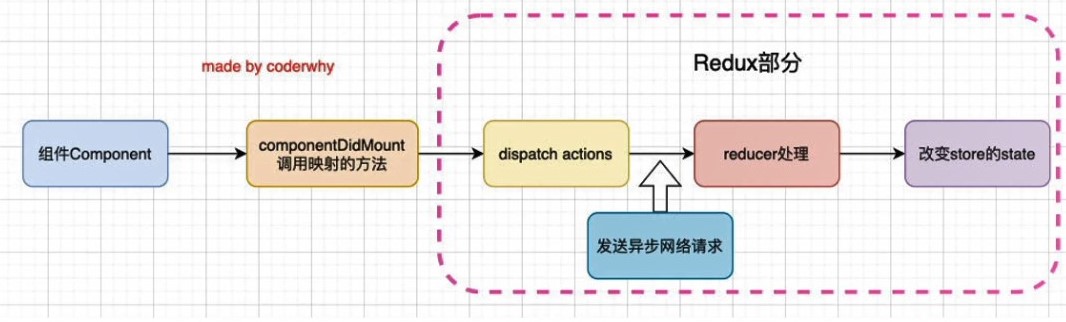
异步请求
网络请求到的数据属于状态管理的一部分,所以请求数据应该由 redux 进行管理。
然而,redux 本身没有异步请求的概念,需要借助中间件进行实现。
redux 中间件的作用是对 store 的 dispatch 方法进行升级,如果传入的是函数,会将函数执行后再进行其他操作。
redux-thunk
官方推荐,用于处理store中的异步事件。
一般使用 actionCreateor 返回的是对象,使用 redux-thunk 后可以返回异步函数,action 为函数,store.dispatch(action) 执行的是函数并获取返回结果。
redux-saga
redux-saga 使用过程中,在 store.dispatch(action)时,store 和 saga 能够同时接收到 action 参数
redux-saga 和 redux-thunk 的作用相同,用法不同。
redux-thunk 提供的接口少,适用于中小型项目。
redux-saga 有丰富的接口,适用于逻辑复杂的大型项目。
中间件
api 文档:https://redux.js.org/api/applymiddleware
redux 使用中间件
store/index.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk'
import reducer from './reducer'
// 应用一些中间件
const storeEnhancer = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware)
const store = createStore(reducer, storeEnhancer)
export default storeactionCreators.js
// redux-thunk 中定义的函数
export const getHomeMultidataAction = dispatch => {
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
const { data: { banner: { list: banners }, recommend: { list: recommends } } } = res.data
console.log(banners)
dispatch(changeBannersAction(banners))
dispatch(changeRecommendsAction(recommends))
})
}实现简单的中间件(中间件原理)
const redux = require('redux')
const actionTypes = {
ADD_NUMBER: 'ADD_NUMBER',
SUB_NUMBER: 'SUB_NUMBER'
}
const actionCreators = {
addAction(num) {
return {
type: actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER,
num
}
},
subAction(num) {
return {
type: actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER,
num
}
},
thunkAction(dispatch, getState) {
dispatch(actionCreators.subAction(1))
console.log('state: ', getState())
}
}
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// reducer
// 默认情况下 初始化state是没有值的,所以此时要赋值初始值
function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter + action.num}
case actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state
}
}
// store (创建的时候需要传入 reducer)
const store = redux.createStore(reducer)
// 调用 ====================================================
// store.dispatch(actionCreators.addAction(10))
// console.log(store.getState())
// 根据需求封装中间件
// 需求:在 dispatch 之前打印一下数据,在 dispatch 之后打印一下数据
// 方式一 创建一个函数进行包裹
// function dispatchAndLogging(action) {
// console.log('dispatch before--dispatching action: ', action)
// store.dispatch(action)
// console.log('dispatch after--new state: ', store.getState())
// }
// dispatchAndLogging(actionCreators.addAction(10))
// 方式二 hack技巧 monkeyingpatch 将原有的api重新进行定义 使用时依旧按照原来的使用方式进行
function patchLogging(store) {
const next = store.dispatch
function dispatchAndLogging(action) {
console.log('dispatch before--dispatching action: ', action)
next(action)
console.log('dispatch after--new state: ', store.getState())
}
store.dispatch = dispatchAndLogging
// return dispatchAndLogging // 使用 applyMiddlewares
}
// 同理 封装 thunk 方法 处理 actionCreator是函数的情况
function patchThunk(store) {
const next = store.dispatch
function dispatchAndThunk(action) {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
action(next, store.getState)
} else {
next(action)
}
}
store.dispatch = dispatchAndThunk
// return dispatchAndThunk // 使用 applyMiddlewares
}
// 封装 applyMiddlewares 需要中间件函数返回纯函数的方式进行
// function applyMiddlewares(...middlewares) {
// middlewares.forEach(middleware => {
// store.dispatch = middleware(store)
// })
// }
// applyMiddlewares(patchLogging, patchThunk)
patchLogging(store) // 装载 store.dispatch
patchThunk(store)
store.dispatch(actionCreators.addAction(10)) // 依旧按照原来的方式进行调用
store.dispatch(actionCreators.thunkAction)实现中间件的一种方式,还有其他方式,可以参考其他 redux 中间件源码。
实战
node + redux
const redux = require('redux')
// 常量
// const actionTypes = {
// INCREMENT: 'INCREMENT',
// DECREMENT: 'DECREMENT',
// ADD_NUMBER: 'ADD_NUMBER',
// SUB_NUMBER: 'SUB_NUMBER'
// }
const actionTypes = {
INCREMENT: Symbol('INCREMENT'),
DECREMENT: Symbol('DECREMENT'),
ADD_NUMBER: Symbol('ADD_NUMBER'),
SUB_NUMBER: Symbol('SUB_NUMBER')
}
// 初始值
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// reducer
// 默认情况下 初始化state是没有值的,所以此时要赋值初始值
function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case actionTypes.INCREMENT:
return {...state, counter: state.counter + 1}
case actionTypes.DECREMENT:
return {...state, counter: state.counter - 1}
case actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter + action.num}
case actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state
}
}
// store (创建的时候需要传入 reducer)
const store = redux.createStore(reducer)
// 订阅 store 的修改 要在派发action之前做
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log('state 发生了修改', store.getState().counter)
})
// actions
const action1 = {type: actionTypes.INCREMENT}
const action2 = {type: actionTypes.DECREMENT}
const action3 = {type: actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER, num: 5}
const action4 = {type: actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER, num: 12}
// 函数方式动态设置传入参数
const action5 = num => {
return {type: actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER, num}
}
// 派发 action 然后执行 reducer纯函数进行处理数据
store.dispatch(action1)
store.dispatch(action2)
store.dispatch(action3)
store.dispatch(action4)
store.dispatch(action5(90))使用 symbol类型定义 action type 不利于 redux devtool 跟踪查看数据变化
react + redux
使用 redux 的组件示例
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import store from '../../store'
import {
increment,
addNumber
} from '../../store/actionCreators'
export default class Home extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
counter: store.getState().counter
}
}
componentDidMount() {
// 订阅
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
counter: store.getState().counter
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 取消订阅
this.unsubscribe()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>Home - 当前计数: {this.state.counter}</h4>
<div>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
<button onClick={e => this.addNumber(5)}>+5</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
increment() {
store.dispatch(increment())
}
addNumber(num) {
store.dispatch(addNumber(num))
}
}抽取 redux 与 组件链接的公共代码
使用 store 进行数据交互
使用高阶组件封装 工具函数
import React, { PureComponent } from "react"
import store from "../store"
/**
* 建立 react 与 redux 的连接
* @param {function} mapStateToProps 组件中需要使用的 store 中的数据映射到 props 中,返回值为对象
* @param {function} mapDispachToProp 组件中需要派发的 action 映射到 props 中,返回值为对象
*/
export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispachToProp) {
// 高阶组件
return function enhanceHOC(WrappedComponend) {
return class extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
// 返回组件中需要的 state
storeState: mapStateToProps(store.getState())
}
}
componentDidMount() {
// 建立监听
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
storeState: mapStateToProps(store.getState())
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 取消监听
this.unsubscribe()
}
render() {
// props 穿透
return <WrappedComponend
{...this.props}
{...mapStateToProps(store.getState())}
{...mapDispachToProp(store.dispatch)} />
}
}
}
}组件使用
import React from 'react'
import connect from '../../utils/connect'
import {
increment,
addNumber
} from '../../store/actionCreators'
function Home(props) {
return (
<div>
<h4>Home - 当前计数: {props.counter}</h4>
<div>
<button onClick={e => props.increment()}>+1</button>
<button onClick={e => props.addNumber(5)}>+5</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
counter: state.counter
}
}
const mapDipatchToProps = dispatch => {
return {
increment() {
dispatch(increment())
},
addNumber(num) {
dispatch(addNumber(num))
}
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDipatchToProps)(Home)进一步优化,抽离 store 数据
减少业务代码耦合,使用 context 进行抽离业务数据。
context.js
import React from 'react'
const StoreContext = React.createContext()
export {
StoreContext
}connect.js
// 优化 connect 工具函数 将 store 利用 context 抽离出去
// 减少业务代码耦合
import React, { PureComponent } from "react"
import { StoreContext } from "./context"
export default function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispachToProp) {
// 高阶组件
return function enhanceHOC(WrappedComponend) {
class EnhanceComponent extends PureComponent {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context)
this.state = {
// 返回组件中需要的 state
storeState: mapStateToProps(context.getState())
}
}
componentDidMount() {
// 建立监听
this.unsubscribe = this.context.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
storeState: mapStateToProps(this.context.getState())
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 取消监听
this.unsubscribe()
}
render() {
// props 穿透
return <WrappedComponend
{...this.props}
{...mapStateToProps(this.context.getState())}
{...mapDispachToProp(this.context.dispatch)} />
}
}
EnhanceComponent.contextType = StoreContext
return EnhanceComponent
}
}父组件使用,将store与context建立连接,提供数据
import React from 'react'
import Home from './Home'
import About from './About'
import { StoreContext } from '../../utils/context'
import store from '../../store'
export default function UseConnect() {
return (
<StoreContext.Provider value={ store }>
<Home></Home>
<About></About>
</StoreContext.Provider>
)
}子组件中和 store 方法一致
相关第三方库
react-redux :官方库,灵活绑定 react 和 redux 。
拆分 reducer
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import * as actionTypes from './actionTypes'
// 初始值
// const initialState = {
// counter: 0,
// banners: [],
// recommends: [],
// }
// function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
// switch (action.type) {
// case actionTypes.INCREMENT:
// return {...state, counter: state.counter + 1}
// case actionTypes.DECREMENT:
// return {...state, counter: state.counter - 1}
// case actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER:
// return {...state, counter: state.counter + action.num}
// case actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER:
// return {...state, counter: state.counter - action.num}
// case actionTypes.CHANGE_BANNERS:
// return {...state, banners: action.banners}
// case actionTypes.CHANGE_RECOMMENDS:
// return {...state, recommends: action.recommends}
// default:
// return state
// }
// }
// reducer 拆分 state 调用的地方需要一起修改
const defaultCounterState = {
counter: 0
}
function counterReducer(state = defaultCounterState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case actionTypes.INCREMENT:
return {...state, counter: state.counter + 1}
case actionTypes.DECREMENT:
return {...state, counter: state.counter - 1}
case actionTypes.ADD_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter + action.num}
case actionTypes.SUB_NUMBER:
return {...state, counter: state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state
}
}
const defaultHomeState = {
banners: [],
recommends: []
}
function homeReducer(state = defaultHomeState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case actionTypes.CHANGE_BANNERS:
return {...state, banners: action.banners}
case actionTypes.CHANGE_RECOMMENDS:
return {...state, recommends: action.recommends}
default:
return state
}
}
// function reducer(state = {}, action) {
// return {
// counterInfo: counterReducer(state.counterInfo, action),
// homeInfo: homeReducer(state.homeInfo, action)
// }
// }
// 最终的结果是 reducer 返回和 state = { counterInfo: {}, homeInfo: {} } 一样的对象格式
// 使用 redux combineReducers(reducers) api 进一步优化
const reducer = combineReducers({
counterInfo: counterReducer,
homeInfo: homeReducer
})
export default reducercombineReducers 函数 将我们传入的 reducers 合并到一个对象中,最终返回一个 combination 的函数,在执行 combination 函数的过程中,它会通过判断前后返回的数据是否相同来决定返回之前的 state 还是新的 state。新的 state 会触发订阅者发生对应的刷新,而旧的 state 可以有效的阻止订阅者发生刷新。
结合 ImmutableJs
ImmutableJs :使用不可变的数据。
redux-immutable:使用 combineReducer 函数结合redux 和 immutable.js 的功能。
fromJS 会进行深层比较,而 map 会进行浅层的比较,根据业务需求来确定使用哪一个 api ,fromJS 的性能会比 map 的性能更低。
更多阅读: https://redux.js.org/faq/immutable-data
性能优化
扩展
生态:https://redux.js.org/introduction/ecosystem
工具
redux devtool :不同的场景需要手动设置使用方式,https://github.com/reduxjs/redux-devtools/tree/master/extension#usage
基础使用方式,需要在创建 store 时声明使用
const store = createStore(
reducer, /* preloadedState, */
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);